×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Kia Parts
- Kia Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
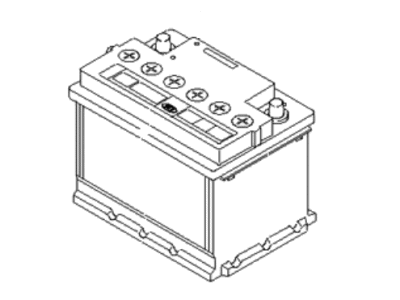
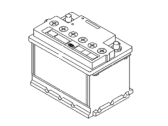
Genuine Kia Spectra Car Batteries
Auto Battery- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
1 Car Batteries found
Kia Spectra Car Batteries
If you're in search of top-notch, reasonably priced OEM Kia Spectra Car Batteries, then you've found the perfect spot. Our website boasts an extensive inventory of Kia Spectra Car Batteries, all priced at the market's premier price. Rest assured, every genuine part we offer comes with a warranty straight from the manufacturer.
Kia Spectra Car Batteries Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to maintain your Kia Spectra's battery through routine preventive maintenance?A:For a powerful start-up, adopting preventive maintenance measures to keep your vehicle's battery working is very important. Before any battery maintenance can be done, ensure that you have the right safety gear which includes face shield/safety goggles, baking soda, petroleum jelly, battery post/cable cleaner, treated felt washers, a puller and rubber gloves. When working on the battery always turn off the engine and disconnect the cable from its negative terminal as a measure to avoid accidents. Be aware of the fact that batteries produce highly flammable and explosive hydrogen gas and contain poisonous sulfuric acid. Do not spark any fire or smoke near it and charge in a well-ventilated place. Wear protective goggles for safety with kids staying away from it while checking external conditions like positive terminal protection (corrosion), loose connections (cracks) and clamps. If there is corrosion then remove the battery for cleaning starting by loosening cable clamp bolts then carefully disconnecting ground cable first. Cleanse cable clamps thoroughly using either battery brush or terminal cleaner plus warm water mixed with baking soda ensuring that corrosions are dealt without overdoing it. Clean terminals as well as the top part of the battery also using this solution taking care not to let it go into your battery while putting on safety goggles, rubber gloves and old clothes during this process. For heavily corroded terminals use a terminal cleaner. Rinse all cleaned areas with plain water; check condition of battery tray ensuring tightly held down clamp fasteners. When returning back the tray ensure no parts were left behind in there together with avoiding over tightening hold-down clamp bolts too much. To get rid of corrosion on hold-down components including around battery case, apply water with baking soda before rinsing all cleaned areas with plain water properly afterwards leaving them bare when done thus giving way to zinc based primer painting damaged metal parts due to corrosion.Battery charging involves slow-rate charging which restores deep discharged cells and maintains charge during infrequent use especially in winter. For safe and low-stress charging, it is best to use a one or two-amp battery charger which is often referred as a "trickle" charger; however, when faster charging is needed then higher amperage charger can be utilized provided that it does not exceed 1/10th of the battery's amp/hour rating. Avoid rapid boost charges which claim to restore the cells within one or two hours because they can damage batteries in poor condition apart from being set aside for emergencies. Generally, these chargers take 12 to 16 hours for a full charge but you have to observe specific charging times according to your charger's instructions.