×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Kia Parts
- Kia Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Kia Sedona Fuse
Circuit Fuse- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
30 Fuses found

Kia Sedona Fuse-Micro 20A
Part Number: 1879005263$2.39 MSRP: $3.42You Save: $1.03 (31%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-150A Main
Part Number: 1898005932$15.77 MSRP: $22.57You Save: $6.80 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-Micro 10A
Part Number: 1879005261$2.66 MSRP: $3.80You Save: $1.14 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-125AMP
Part Number: 1898005931$20.78 MSRP: $29.73You Save: $8.95 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-Micro 15A
Part Number: 1879005262$0.79 MSRP: $1.13You Save: $0.34 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-Micro 30A
Part Number: 1879005265$2.67 MSRP: $3.82You Save: $1.15 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days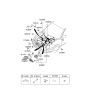
Kia Sedona Fuse-60A Main
Part Number: 1898005927$21.94 MSRP: $29.73You Save: $7.79 (27%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-Micro 25A
Part Number: 1879005264$2.67 MSRP: $3.82You Save: $1.15 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-Slow Blow 120AM
Part Number: 1898006575$15.37 MSRP: $21.98You Save: $6.61 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-Slow Blow 40A
Part Number: 1898004825$7.76 MSRP: $11.10You Save: $3.34 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Sedona Fuse-Slow Blow Micro
Part Number: 1879004934$9.40 MSRP: $13.45You Save: $4.05 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days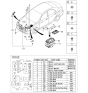
Kia Sedona Fuse-Slow Blow 20A
Part Number: 1898004823$14.62 MSRP: $20.92You Save: $6.30 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Sedona Fuse-Micro 75A
Part Number: 1879005260$4.78 MSRP: $6.83You Save: $2.05 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Sedona Fuse-Mini
Part Number: 1898004815$4.78 MSRP: $6.83You Save: $2.05 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Sedona Fuse-Mini
Part Number: 1898004819$4.78 MSRP: $6.83You Save: $2.05 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Sedona Fuse-Slow Blow Micro
Part Number: 1879004933$9.40 MSRP: $13.45You Save: $4.05 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Sedona Fuse-Mini
Part Number: 1898004814$5.04 MSRP: $6.83You Save: $1.79 (27%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Sedona Fuse-Mini 10A
Part Number: K997061110$5.04 MSRP: $6.83You Save: $1.79 (27%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Sedona Fuse-Mini 15A
Part Number: K997061115$5.04 MSRP: $6.83You Save: $1.79 (27%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 30 Results
Kia Sedona Fuse
If you're in search of top-notch, reasonably priced OEM Kia Sedona Fuse, then you've found the perfect spot. Our website boasts an extensive inventory of Kia Sedona Fuse, all priced at the market's premier price. Rest assured, every genuine part we offer comes with a warranty straight from the manufacturer.
Kia Sedona Fuse Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How are the electrical circuits of a Kia Sedona safeguarded, and what should be considered when replacing fuses?A:The electrical systems of the vehicle are protected by fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links with current cars having several fuse and relay boxes incorporated. In a car, there is always any specific fuse; every fuse is located at different places, irrespective of the fact that the main fuse/relay panel is placed in the engine compartment; however, every fuse safeguards a particular circuit that is named on the fuse panel legend. The fuse box has become complicated with more than one site for fuses and relays and perhaps non-servicing micro-processors and internal connections, therefore if they become a problem, it is all or nothing. For the cars produced in 2005 and earlier, the location of the passenger compartment fuse box is at the driver's side of the car. There is the left kick panel fuse box, and the engine compartment fuse box is situated behind the battery, but under the hood. For 2006 and next years the passenger compartment fuse box is located in the driver's side knee bolster panel, while extra modules are situated in the front and rear part of the automobile. Fuses vary in size and kind which located at fuse blocks, and when an electrical component fails, one has to look at the fuses because they may be the problem using a test light to identify whether a fuse has gone off. Fuses that have been blown should be replaced with the correct types; this is because wrong rating circuits affect the protection of the circuits. If, for instance, replacement of a fuse leads to its failure as soon as again, then the problem should be resolved probably by constricting a short circuit before trying another switch again. Some circuits have fusible links that are used in high current; an indication is a bulge in the cable or cartridge type links in the engine compartment and fuse and relay box and these can be replaced by units of the same amperage while the negative battery terminal is disconnected.