×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Kia Parts
- Kia Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
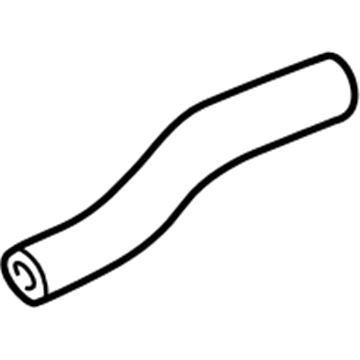
Genuine Kia Spectra PCV Hose
PCV Valve Hose- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
9 PCV Hoses found

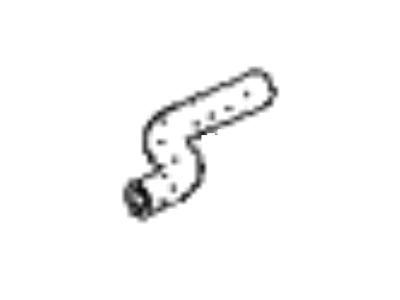
Kia Spectra Hose-PCV
Part Number: 0K2A513895$5.79 MSRP: $7.85You Save: $2.06 (27%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
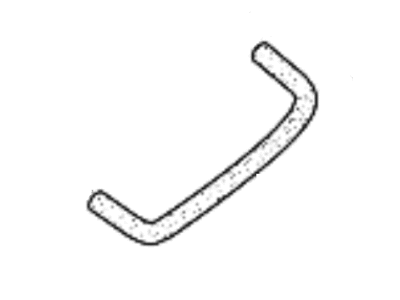
Kia Spectra Hose-PCV
Part Number: 267212Y002$10.92 MSRP: $15.62You Save: $4.70 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysKia Spectra Hose-PCV
Part Number: 267212Y001$11.53 MSRP: $15.62You Save: $4.09 (27%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Kia Spectra PCV Hose
If you're in search of top-notch, reasonably priced OEM Kia Spectra PCV Hose, then you've found the perfect spot. Our website boasts an extensive inventory of Kia Spectra PCV Hose, all priced at the market's premier price. Rest assured, every genuine part we offer comes with a warranty straight from the manufacturer.
Kia Spectra PCV Hose Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What is the purpose of the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system,PCV Hose and PCV valve on Kia Spectra?A:The PCV system is a good way of reducing hydrocarbon emissions by scavenging crankcase vapors. It circulates fresh air through the crankcase that comes in from the air intake duct to mix with blow-by gases before being pulled into the intake manifold by means of a PCV valve and vacuum in the manifold. The two main constituents of the PCV system are a pair of hoses and the PCV valve. The fresh air inlet hose begins its travel at the throttle body or air intake duct, then onto this pipe located on top of the valve cover. This combination is then taken up from beneath using an inchmanifold vacuum inch through both pressure release valves (PCV) and crank case ventilation hose (cvh). Whenever manifold vacuum is high and engine idle quality must be maintained, for instance upon engine start-up, or during deceleration, a ball and spring check-valve closes with low flows enough to restrict flow out of the crank-case through any other path than the PCV assembly into Manifold vacuum which may drop as low as 10 inches-of-mercury (in Hg). For four cylinders cars you can disconnect fresh air inlet hose from throttle body or air intake duct or remove it from valve cover. When you want to disconnect it from pcv valve or intake manifold just pull off Crankcase Ventilation Hose. In Sportage V6 models, loosen both ends of fresh air inlet hose and crank case ventilation hose so that they can be removed easily. Remove the PVC valve from front Valve Cover.